This module contains routines to generate and operate on arrays
- Utilities for array manipulation and simple calculations
- Grid creation There are a few functions to quickly create arrays.
- Search and sort: Functions for search an element in a sorted array, and sort arrays.
- Generation of histograms. Do we want histogram2d?
Array utils
This submodule provides a few convenience routines to work with arrays
- function array_utils::allclose() Returns .True. if two arrays are element-wise equal within a tolerance.
- subroutine array_utils::save_array() Stores an array to file or stdout
- function array_utils::mean() Computes the arithmetic mean of the array.
- function array_utils::std() Computes the standard deviation of the array.
- function array_utils::merge_sorted() Creates a sorted array with values from two input sorted arrays
Grids
This submodule provides convenience routines to create commonly occurring grids, somewhat mimicking those appearing in Numpy:
- grids::linspace() returns evenly (linearly) spaced numbers over a specified interval.
- grids::logspace() and grids::geomspace() return logarithmically evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval.
- grids::loglinspace() returns spaced numbers that are approximately logarithmically spaced for smaller values and approximately linear at large values.
- grids::arange() returns an array of integer numbers from a given interval.
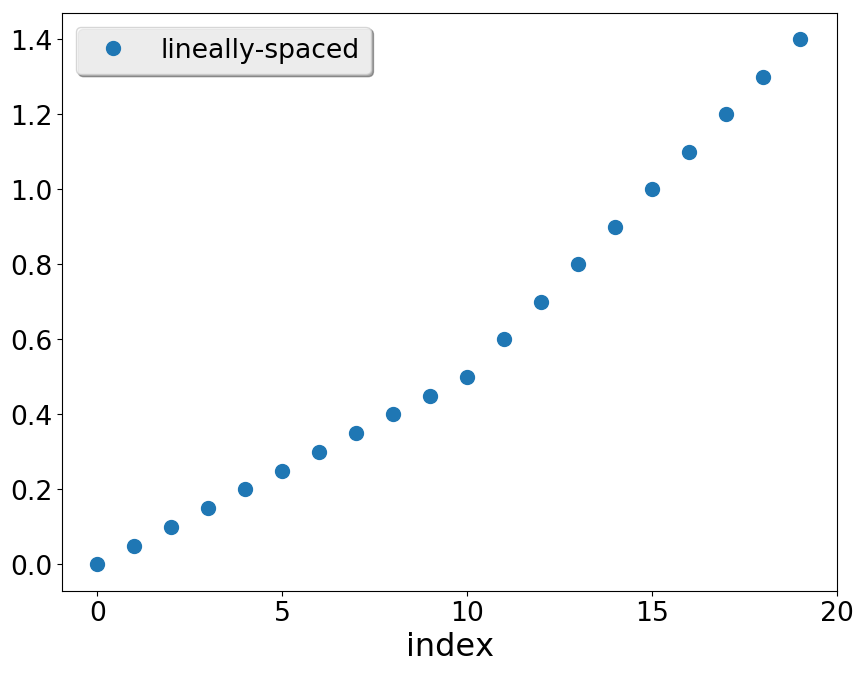
Equally spaced grids
The signature of linspace is:
This means (compare to documentation of numpy.linspace):
- The name of the function is linspace
- start: The first value of the sequence desired
- end: The end value of the sequence, unless endpoint is set to False. In that case, the sequence consists of all but the last of num + 1 evenly spaced samples, so that stop is excluded. Note that the step size changes when endpoint is False.
- num: Number of samples to generate. Note: it is required not optional.
- endpoint: (boolean, optional). If .True., end is the last sample. Otherwise, it is not included. Default is .True.
- retstep: (optional). If present will have the value of step on output.
Prints
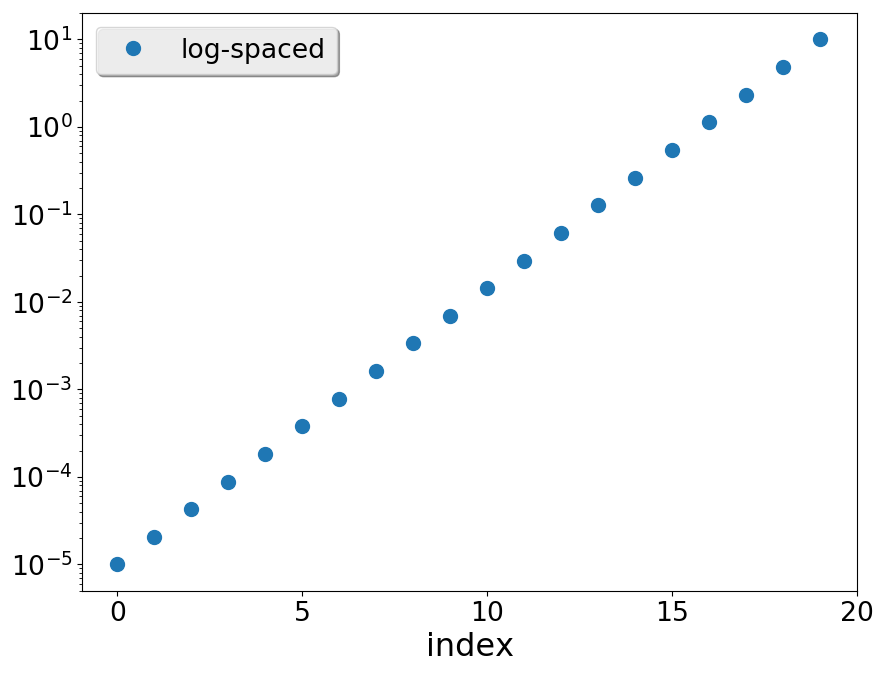
Logarithmic spaced grids
There are two different functions returning grids with data equispaced in a logarithmic scale.
The function logspace(), takes as arguments the exponents of the endpoints, while geomspace() takes directly the endpoints. Their signature are:
where:
- The interval spans between base**start and base**end
- endpoint indicates if the final point end will be included, like in linspace.
- base of the log space. By default is 10.
being the only difference that now the interval spans between start and end
Prints
Logarithmic-linearly spaced grids
The routine loglinspace() produces grids with different behavior depending on the values of step and ratio.
It is nearly uniform, with spacing approximately step when ratio 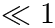
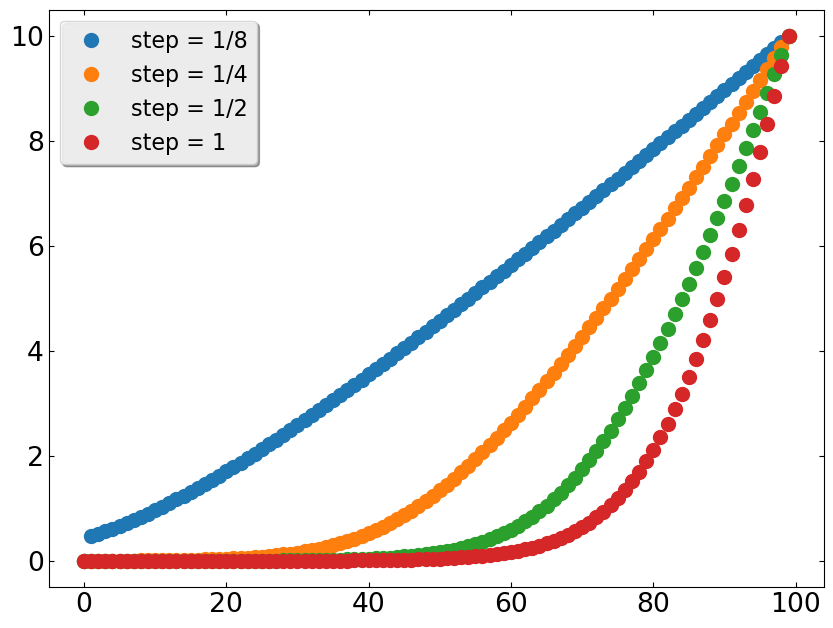
Search and sort of arrays
There are routines implemented for sorting and search sorted arrays.