Subroutine qnthsh implements integration by tanh-sinh method. More...
Detailed Description
Subroutine qnthsh implements integration by tanh-sinh method.
This routine is a simple non-adaptive automatic integrator using trapezoidal rule to integrate a the transformed integrand using the double exponential (also called tanh-sinh) method. The tahn-sinh scheme is based on the observation that the trapezoid rule converges very rapidly for functions on the entire real line that go to zero like exp( - exp(t) ). The change of variables 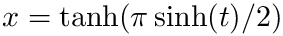
The transformed integral is infinite, but we truncate the domain of integration to [-a, a] ( 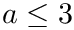
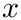
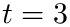
The integration first applies the trapezoid rule to ![$[-a, a]$](form_30.png)
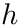
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tanh-sinh_quadrature
- Bailey, David H, "Tanh-Sinh High-Precision Quadrature", 2006
- Cook, John D, "Double Exponential Integration"
- Parameters
-
[in] f a real or complex function (as defined in Integrable functions) [in] a (real(dp)) are the limits of integration [in] b (real(dp)) are the limits of integration [out] IntValue (real or complex, depending on f) Estimated value of the integral [in] epsabs (real, optional) absolute desired precision. Default: epsabs=1.e-7 [in] epsrel (real, optional) relative desired precision. Default: epsrel=1.e-5 [out] abserr (real, optional) absolute estimated error [out] Neval (integer, optional) Number of function evaluations
Example:
The documentation for this interface was generated from the following file:
- /home/fiol/Trabajos/fortran/numfor/src/integrate/tanhsinh.f90